Gynecological & Cervical Cancer Screening
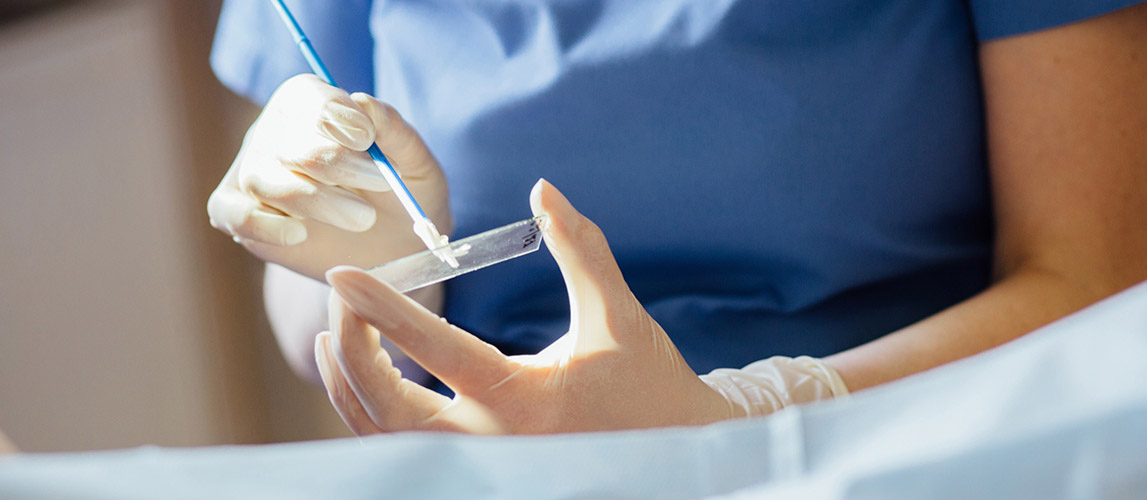
Gynecological screening tests are used to look for diseases before there are any symptoms. Cancer screening tests are effective and can lead to more effective treatment Of all gynecological cancers, only cervical cancer can be effectively screened via tests (the Pap smear and HPV tests) to detect early stages of cancer when treatment can be most effective.
Cervical Cancer screening tests
- Pap smear test
- HPV test
What is the Pap smear test?
A Pap smear is a simple test that looks for changes in cells on the cervix that could turn into cancer if left untreated.
What is the HPV test?
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common virus that can be transmitted through skin-to-skin or sexual contact.
While there are more than 100 types of HPV, 70% of infections that lead to cervical cancer are caused by HPV types 16 and 18.
The human papillomavirus (HPV) test looks for the virus high-risk HPV types 16 and 18 as well as 12 other high-risk types that cause changes in cervical cells.
Early detection of HPV is key to preventing the majority of cervical cancers from ever occurring. The HPV test also screens for 12 other high-risk HPV types.
Why Test for HPV?
International guidelines now show the best way to screen for cervical cancer risk is to test for HPV—which causes 99% of all cervical cancers.
Testing for high-risk HPV is more effective than a Pap test for the detection of cervical pre-cancer.
Family Medical Practice and Care1 are now offering the HPV screening test, one of the most accurate ways to distinguish between high and low risk of developing cervical cancer.
For more information about the HPV screening test, please speak with our gynecologist. You may also obtain the flyer at reception.
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer affects the cervix, the lowermost part of the uterus.
As with breast cancer, the initial stages of cervical cancer are painless, so women may not know that they have it. Regular screening detects abnormal changes in the cervical cells, thereby preventing cancer from developing.
What are the symptoms?
If you experience the following, see your doctor immediately:
– Vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
– Irregular bleeding between periods or after menopause
– Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
Who is at risk?
All women aged between 25 and 69 who:
– Are sexually active
– Have had multiple sexual partners
– Have had sexually transmitted infections (for example: genital warts, genital herpes and human papillomavirus infection)
– Smokers
| CHECKS INCLUDED |
|---|
| A. COMPREHENSIVE MEDICAL HISTORY & PHYSICAL EXAMINATIONS |
| • Present complaints (if any) • Past medical, family, social & drug history |
| B. INVESTIGATIONS |
| • Consultation and gynecology examination • Cervical cancer screening • Wet mount • Pelvic ultrasound |
| C. MEDICAL REPORT |
| • Detailed medical and family history. • Discussion and interpretation of all laboratory results. • Recommendation of healthcare education and healthcare improvement. • Medical follow-up and direct referrals to other specialists’ services. |
If you would like to make a booking or request more information, please click here or call +84 28 3514 075
To prepare for a gynecological screening, please click here for more information
 We use cookies on this website to enhance your user experience
We use cookies on this website to enhance your user experience